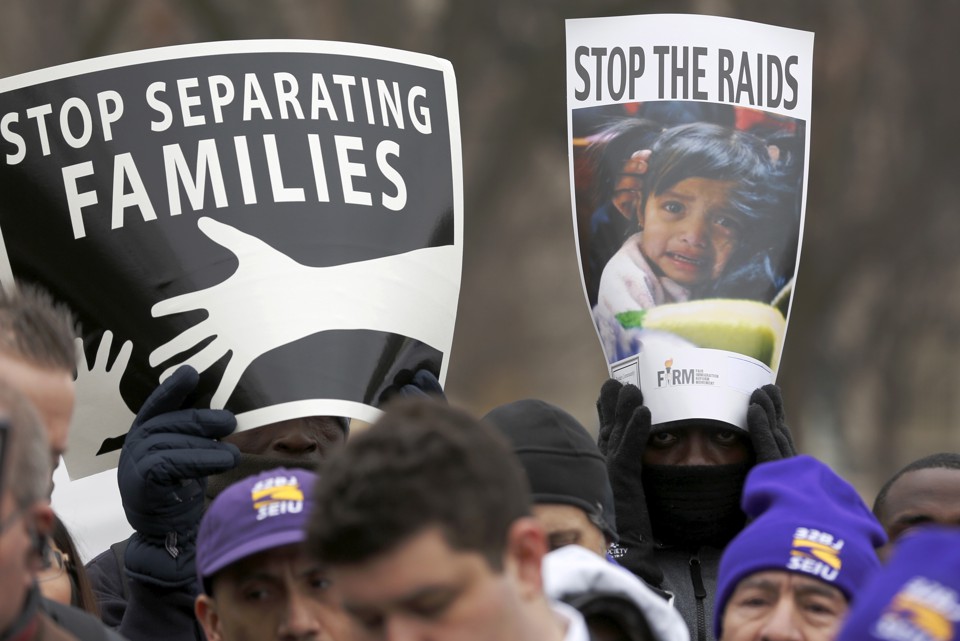
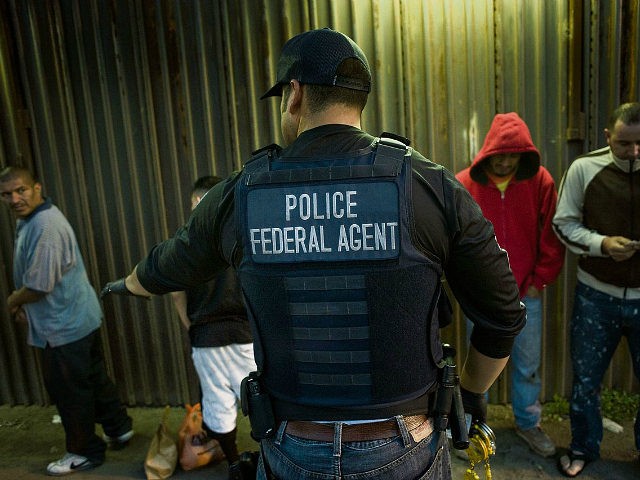
Erik Ortiz reported that a federal operation to arrest undocumented immigrants netted nearly 500 people in cities and states that have openly opposed the Trump administration’s deportation initiatives.
According to Ortiz, Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) officials said last Thursday that its four-day “Operation Safe City” targeted people in residing in the so-called “Sanctuary Cities” of New York, Los Angeles, Philadelphia, Denver, Washington and Baltimore as well as Cook County, Illinois; Santa Clara County in California’s Bay Area; Portland, Oregon; and Massachusetts.
Officials in those places — some referring to themselves as “sanctuary communities” — have been vocal about not fully cooperating with federal immigration authorities, at times clashing with state leaders who support President Donald Trump’s agenda. Sanctuary communities have passed ordinances limiting compliance with federal immigration laws and seek to shield undocumented immigrants who may be deported simply over their immigration statuses or low-level criminal offenses.
“Sanctuary jurisdictions that do not honor detainers or allow us access to jails and prisons are shielding criminal aliens from immigration enforcement and creating a magnet for illegal immigration,” Tom Homan, ICE’s acting director, said in a statement. “As a result, ICE is forced to dedicate more resources to conduct at-large arrests in these communities.”
It is not unusual for ICE to round up immigrants by the hundreds or even low thousands, although the latest raid comes on the heels of a planned operation that would have targeted about 8,400 undocumented immigrants this month.
But the Department of Homeland Security scrapped the operation after the agency said it was halting nationwide enforcement actions in the wake of hurricanes Irma and Harvey. This latest effort indicates the administration is ready to renew its efforts.
“ICE’s goal is to build cooperative, respectful relationships with our law enforcement partners to help prevent dangerous criminal aliens from being released back onto the streets,” Homan said.
According to ICE, of the 498 people arrested this week, 317 had criminal convictions. Some were also categorized as “immigration fugitives,” “previously deported criminal aliens,” and/or associated with a gang.
Most of the criminal convictions were for driving under the influence as well as assault- and drug-related offenses, ICE said. Others were arrested for marijuana possession, traffic offenses and even charges of being a “peeping tom.”
City officials declared Portland a sanctuary city in March, and its mayor, Ted Wheeler, has criticized the Trump administration’s push to end the Obama-era program that has allowed undocumented immigrants who came to the United States as children to remain in the country.
The administration, meanwhile, has faced setbacks as it seeks to overhaul immigration — an issue that has failed repeatedly to gain traction in Congress. Weeks ago, a U.S. district judge in northern Illinois gave sanctuary cities a temporary victory, saying the Justice Department can’t withhold public safety grants to Chicago because officials there don’t want to impose certain immigration policies.
My opinion? As a criminal defense attorney, my role is to protect people’s Constitutional Rights under the Fourth Amendment. Therefore, I have a natural inclination to prevent warrantless, unlawful searches and seizures.
That said, I understand if the government declares a state of emergency holding that exigent circumstances warrants the immediate seizure and deportation of undocumented immigrants.
However, there’s lots of controversy surrounding the subject of ICE raids on Sanctuary Cities. Some civil rights advocates say the raids fit with the Trump administration’s pattern of scapegoating, criminalizing, and demonizing immigrants. Also, courts have said that holding someone without a warrant could violate their constitutional rights, putting jailers at risk of lawsuits. Finally, others have accused Trump’s attack on sanctuary cities as a malignant executive power grab that subverts the Spending Clause and tramples the 10th Amendment.
Please contact my office if you, a friend or family member are charged with a crime. Hiring an effective and competent defense attorney is the first and best step toward justice.