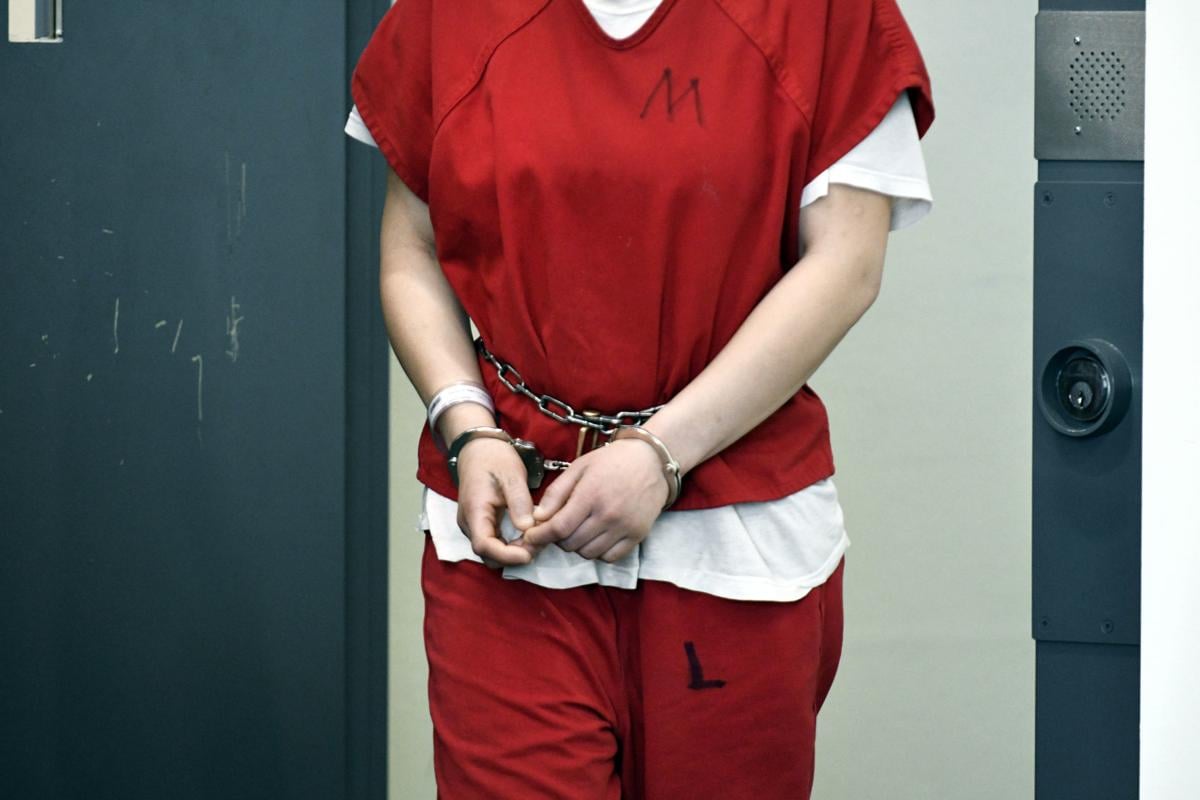
In State v. Jackson, the WA Supreme Court held that shackling in court without analyzing whether the shackles are necessary violates the defendant’s constitutional rights.
BACKGROUND FACTS
In 2017, Mr. Jackson, was charged with assault in the second degree, domestic violence, for strangling his fiancée. At every court appearance, Jackson was forced to wear some form of restraints pursuant to jail policy. The trial court did not engage in any individualized determination of whether restraints were necessary for courtroom safety but, instead, filed a consolidated opinion adopting the jail policy for all superior court appearances for all incarcerated defendants.
After a jury found Jackson guilty, he appealed, arguing that his constitutional right to due process was violated when he was forced to wear restraints without an individualized inquiry into their necessity.
The Court of Appeals held that the shackling of Jackson without an individualized inquiry into whether shackles were necessary violated his constitutional rights. However, it also held that this violation was harmless; thus leaving Jackson with a constitutional violation without a remedy.
Both the Prosecutor and Mr. Jackson appealed to the WA Supreme Court. Jackson argued that the Court of Appeals did not apply the constitutional “harmless error test” correctly. The State, on the other hand, cross-petitioned for review of the constitutionality of the use of pretrial restraints.
COURT’S ANALYSIS & CONCLUSIONS
The WA Supreme Court reviewed the history of defendants wearing pretrial restraints in court:
“The problems in the history of shackling in early America are not limited to the courts and incarcerated individuals . . . The use of shackling as a means of control and oppression, primarily against people of color, has run rampant in the history of this country . . . Shackles and restraints remain an image of the transatlantic slave trade and the systematic abuse and ownership of African persons that has endured long beyond the end of slavery.
Shackles and restraints also represent the forced removal of Native people from their homelands through the Trail of Tears and the slave labor of Native people. We recognize that although these atrocities occurred over a century ago, the systemic control of persons of color remains in society, particularly within the criminal justice system.” ~WA Supreme Court
Next, the Court reasoned that under the Sixth and Fourteenth Amendments to the United States Constitution and article I, section 22 of the Washington State Constitution, it is well settled that a defendant in a criminal case is entitled to appear at trial free from all bonds or shackles except in extraordinary circumstances.
That said, the WA Supreme Court also mentioned that the right to be free from restraint is not absolute, and trial court judges are vested with the discretion to give measures that implicate courtroom security, including whether to restrain a defendant in some capacity in order to prevent injury.
Next, the court identified several factors under State v. Hartzog which help a trial court determine if a defendant needs to be shackled:
“The seriousness of the present charge against the defendant; defendant’s temperament and character; his age and physical attributes; his past record; past escapes or attempted escapes, and evidence of a present plan to escape; threats to harm others or cause a disturbance; self-destructive tendencies; the risk of mob violence or of attempted revenge by others; the possibility of rescue by other offenders still at large; the size and mood of the audience; the nature and physical security of the courtroom; and the adequacy and availability of alternative remedies.” ~WA Supreme Court quoting State v. Hartzog
The Court reasoned that a trial court must engage in an individualized inquiry into the use of restraints prior to every court appearance. Furthermore, the State does not meet this burden by simply establishing that no jurors observed the restraints during trial.
“When the State does not meet its burden to prove that the use of restraints at trial was harmless beyond a reasonable doubt, the defendant is entitled to a new trial and the defendant may only be restrained or shackled during any stage of the proceedings after the court makes an individualized inquiry into whether shackles or restraints are necessary,” said the Court.
With that, the WA Supreme Court reversed the Court of Appeals on harmlessness and remanded for a new trial with instructions that at all stages of court proceedings, the court shall make an individualized inquiry into whether shackles or restraints are necessary.
My opinion? Good decision. The manner in which the justice system treats people in these public settings matters for the public’s perception, including that of the defendant. Practices like routine shackling are inconsistent with our constitutional presumption that people who have not been convicted of a crime are innocent until proven otherwise.
Please contact my office if you, a friend or family member are charged with a crime. Hiring an effective and competent defense attorney is the first and best step toward justice.