Fortune.com reports that millions of people in the U.S. use marijuana daily or nearly every day. This information comes via analysis of national survey data. Also, marijuana users now outnumber alcohol drinkers.
Alcohol is still more widely used, but 2022 was the first time this intensive level of marijuana use overtook daily and near-daily drinking, said the study’s author, Jonathan Caulkins, a cannabis policy researcher at Carnegie Mellon University.
“A good 40% of current cannabis users are using it daily or near daily, a pattern that is more associated with tobacco use than typical alcohol use,” ~Jonathan Caulkins.
THE RESEARCH DATA
The research, based on data from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health, was published Wednesday in the journal Addiction. The survey is a highly regarded source of self-reported estimates of tobacco, alcohol and drug use in the United States.
In 2022, an estimated 17.7 million people reported using marijuana daily or near-daily compared to 14.7 million daily or near-daily drinkers, according to the study. From 1992 to 2022, the per capita rate of reporting daily or near-daily marijuana use increased 15-fold. Caulkins acknowledged in the study that people may be more willing to report marijuana use as public acceptance grows, which could boost the increase.
Most states now allow medical or recreational marijuana, though it remains illegal at the federal level. In November, Florida voters will decide on a constitutional amendment allowing recreational cannabis, and the federal government is moving to reclassify marijuana as a less dangerous drug.
Research shows that high-frequency users are more likely to become addicted to marijuana, said Dr. David A. Gorelick, a psychiatry professor at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, who was not involved in the study.
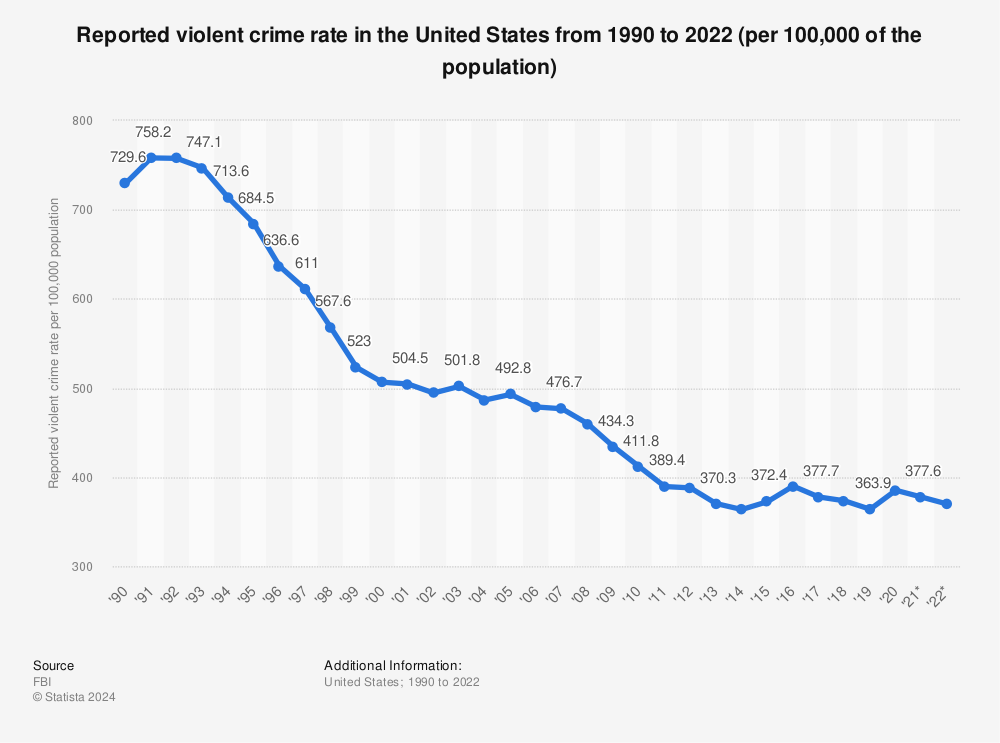
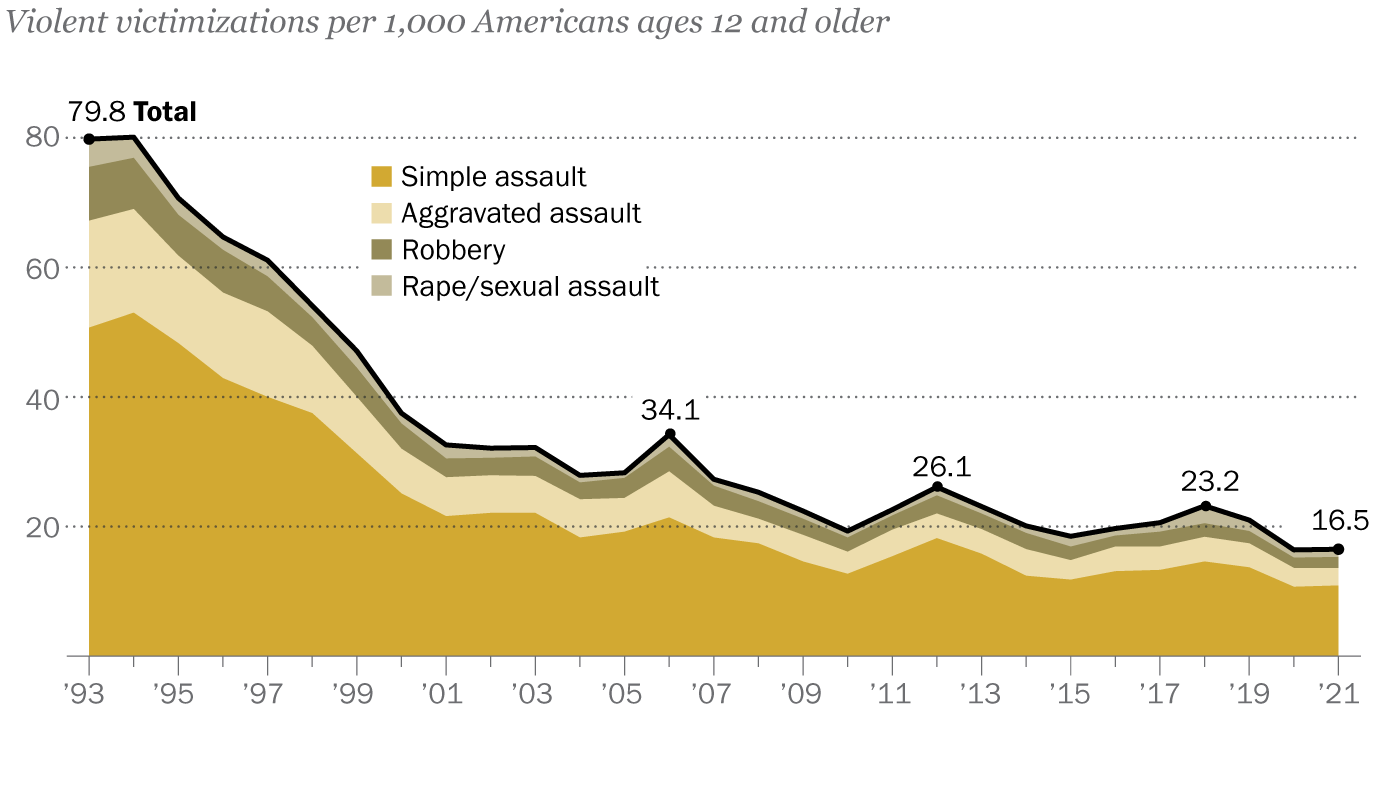
EXCESSIVE DRUG AND ALCOHOL USE LEADS TO CRIMINAL BEHAVIOR
My opinion? The correlation between substance abuse and violent behavior has been well documented. Studies show that more than 26% of respondents who reported using alcohol, cannabis, and cocaine in a 12-month period, also reported committing a violent crime within the same time frame.
Some individuals use aggressive techniques to steal money to buy more drugs; others may be involved in the drug-trafficking, which often leads to violent crimes. For others, violence is a long-term side effect of the substance they abuse. Studies reveal individuals addicted to methamphetamine, for instance, may suffer from anxiety, confusion, insomnia, mood disorders, and aggressive or violent behavior.
Please contact my office if you, a friend or family member are charged with a crime. Hiring an effective and competent defense attorney is the first and best step toward justice.